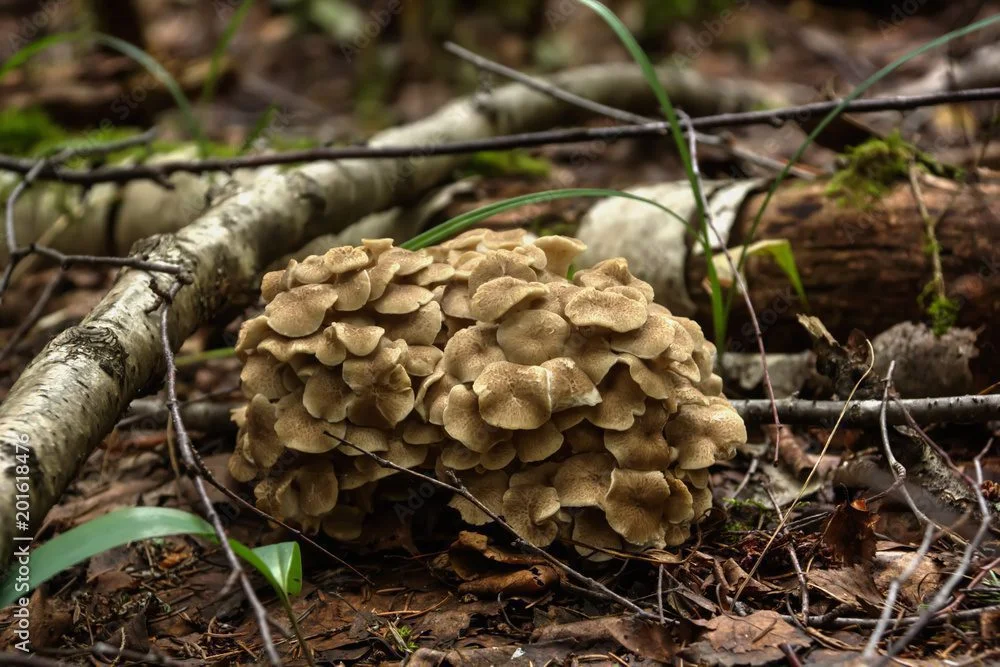
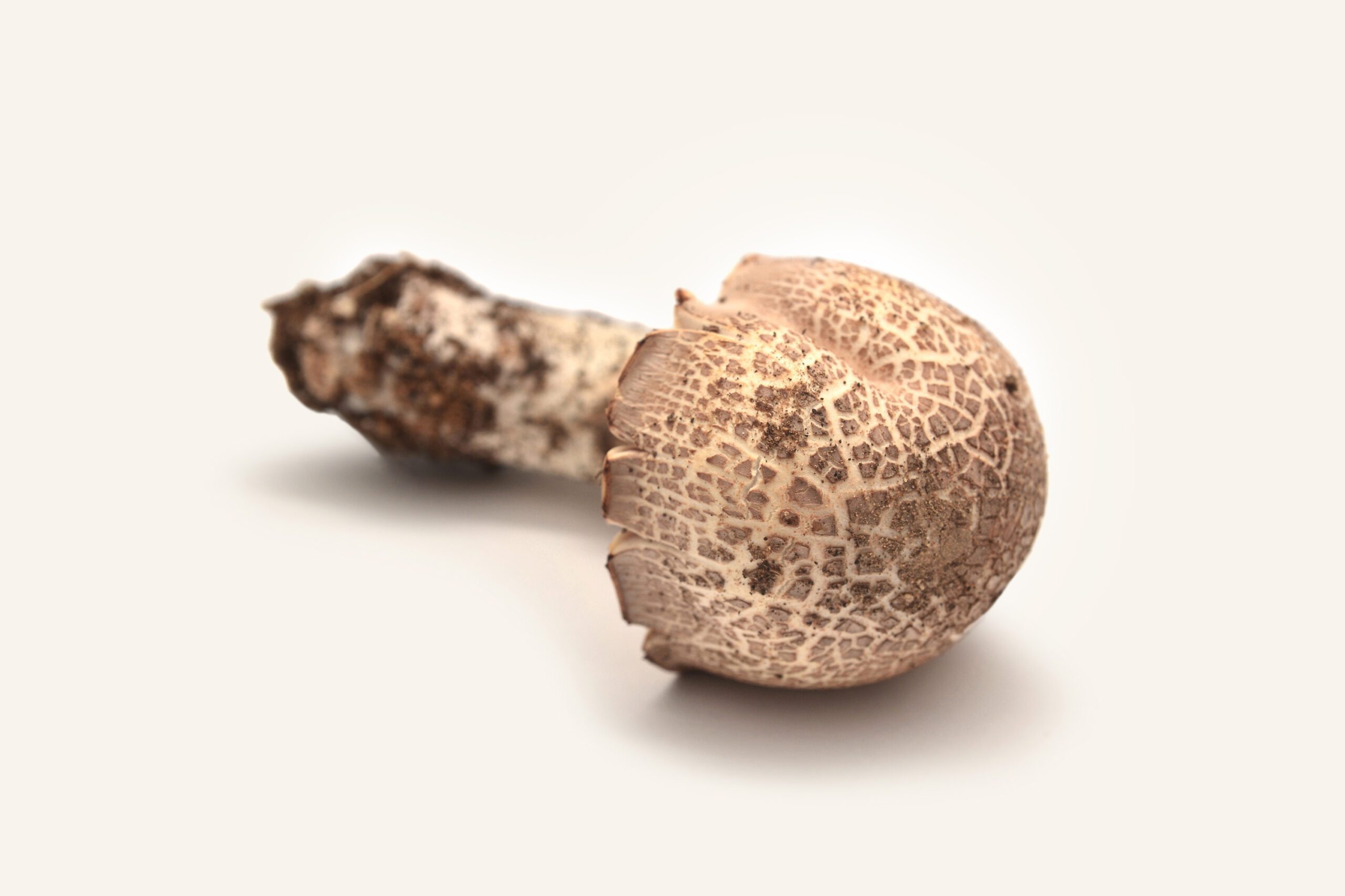
The maitake mushroom's history can be traced back thousands of years, particularly in China and Japan, where it was highly valued for its unique flavor and potential health benefits. The name "maitake" means "dancing mushroom" in Japanese, and it is said to have earned this nickname because people would dance with joy upon discovering this precious fungus in the wild.
Maitake mushrooms have also played a significant role in traditional Chinese medicine, where they were believed to have various medicinal properties. However, due to its scarcity in the wild, only the wealthiest individuals and members of royalty could afford to enjoy this coveted mushroom.
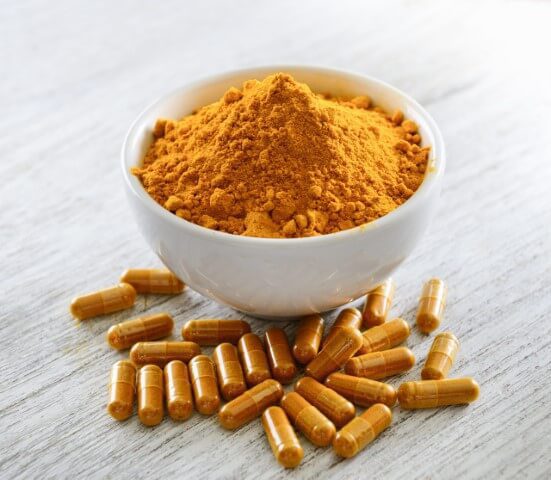
As cultivation techniques improved over time, maitake mushrooms became more widely available, allowing more people to enjoy its unique taste and potential benefits. Nowadays, maitake mushrooms are not only enjoyed as a culinary delight but are also available in supplement form, making it easier than ever to incorporate this ancient fungus into our daily lives.
Maitake mushrooms contain an impressive array of nutrients that contribute to their unique properties. Some of the key nutrients found in maitake mushrooms include:
- Vitamins: Maitake mushrooms are an excellent source of several vitamins, including B-complex vitamins such as riboflavin, niacin, and pantothenic acid. These vitamins play a crucial role in energy production, brain function, and maintaining healthy skin.
-Minerals: Maitake mushrooms are also contain essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium. These minerals are vital for maintaining healthy bones, nerve function, and muscle health.
-Dietary Fiber: Like other mushrooms, maitake is a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and supports a healthy gut microbiome.
-Antioxidants: Maitake mushrooms contain various antioxidants, such as ergothioneine and selenium, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
-Beta-Glucans: Maitake is particularly well-known for its high concentration of beta-glucans, a type of polysaccharide that has been the subject of extensive research for its potential health-promoting properties.